-40%
1960 Vintage Logarithmic Ruler KL-1 Round Made in USSR
$ 20.59
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
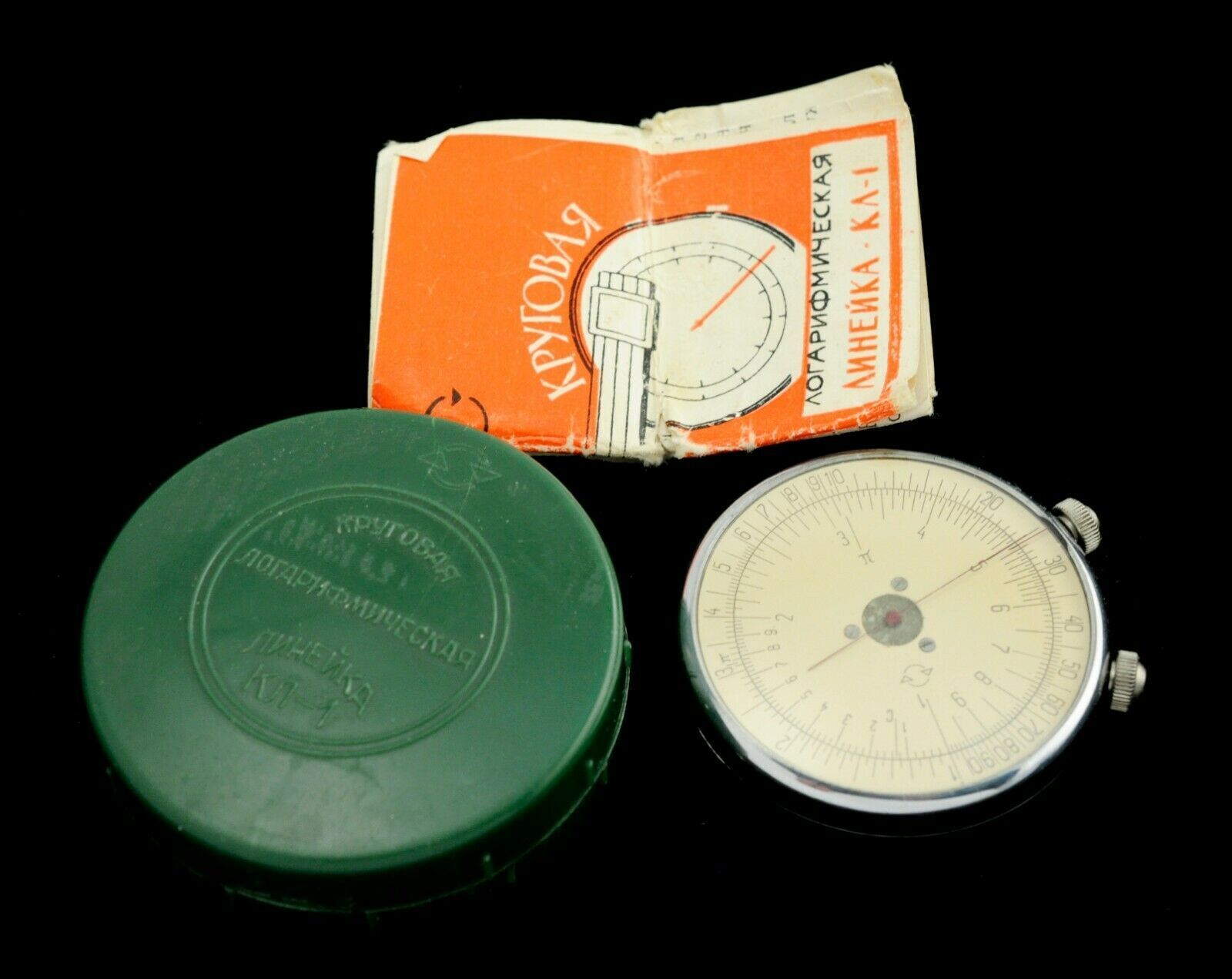
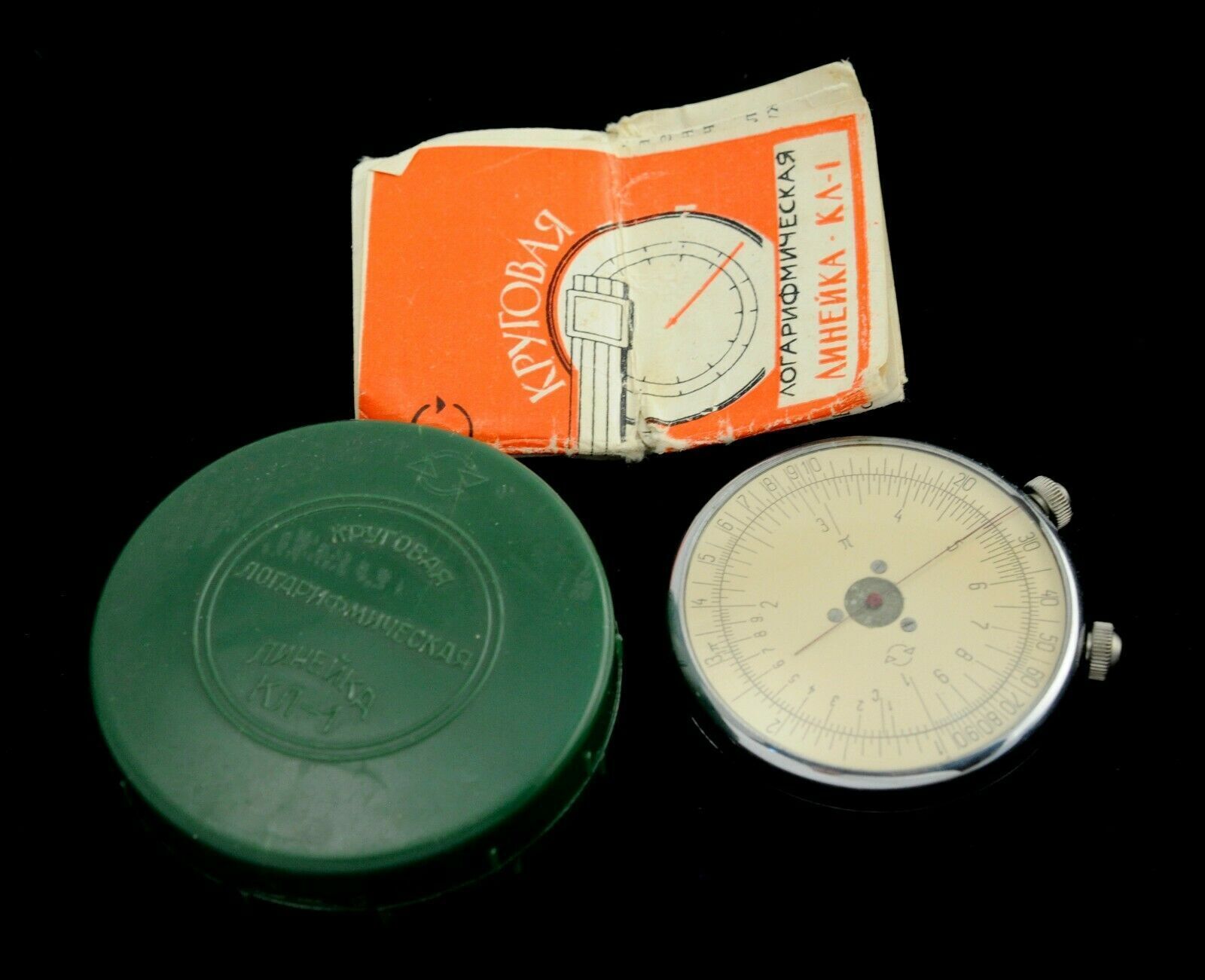
ATTENTION: Dear Customers, you will receive exactly the same item which you see on the pictures, not similar or other. Please read the description carefully and review the photos.Rare Soviet Logarithmic Slide Rule KL-1 made in USSR 1960
You are getting:
Ruler, instructions for use, packing box
ATTENTION! Pulling the heads out of the housing is not allowed.
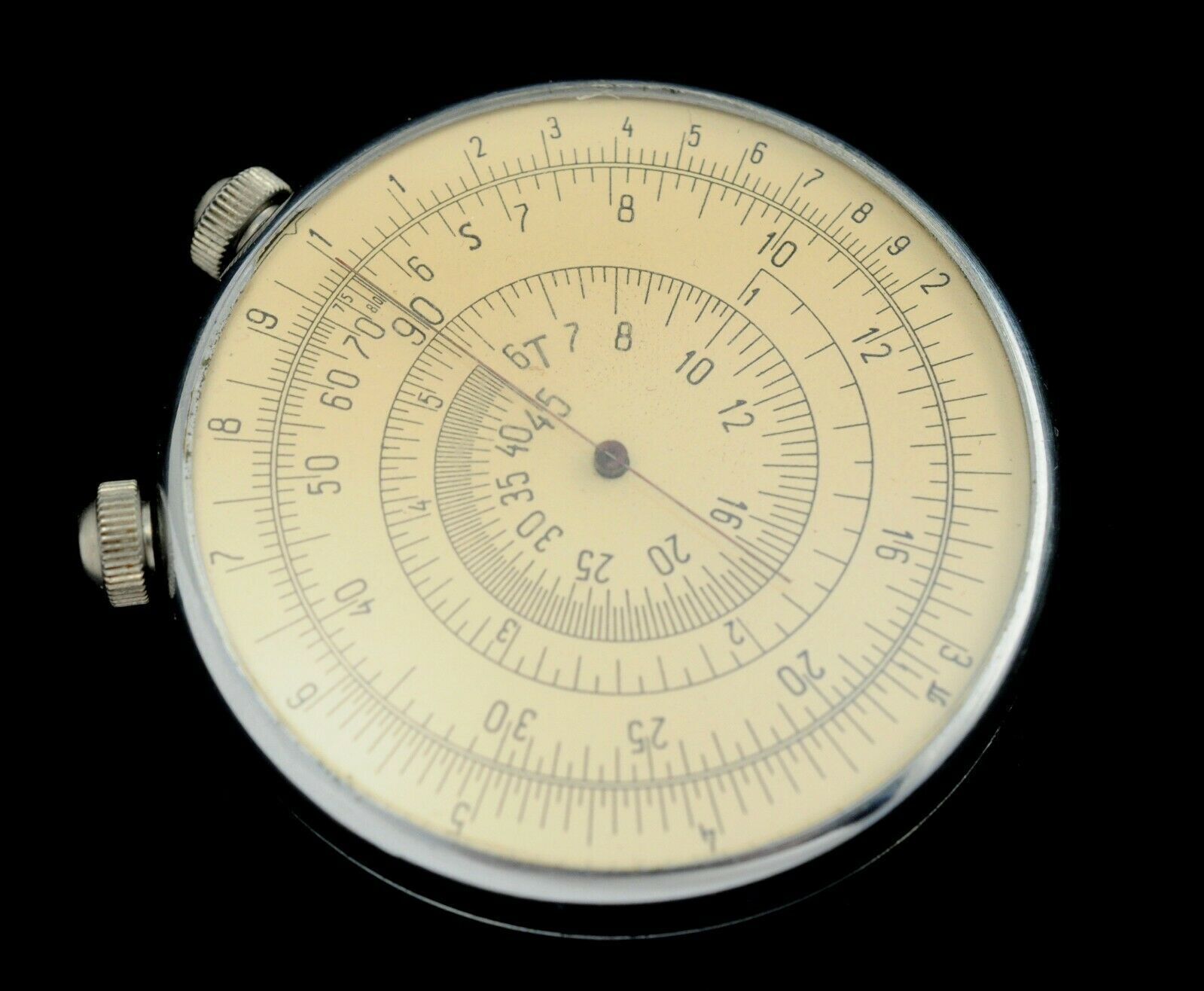
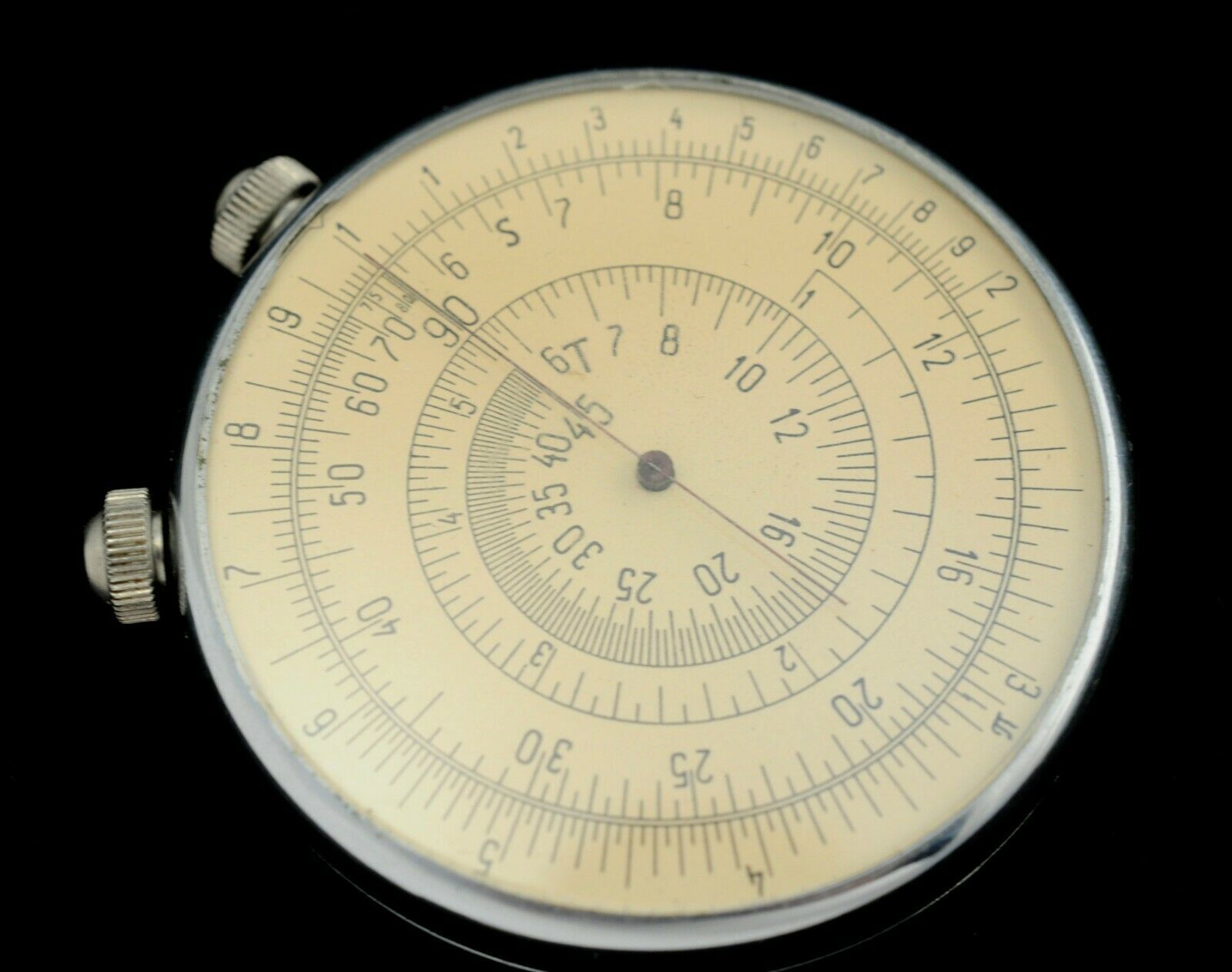
The circular logarithmic ruler "KL-1" is designed to perform the most frequently occurring mathematical operations: multiplication, division, combined actions, erection in the cladrate, extraction of the square root, finding the trigonometric functions of the sine and tangent, as well as the corresponding inverse trigonometric functions, Circle.
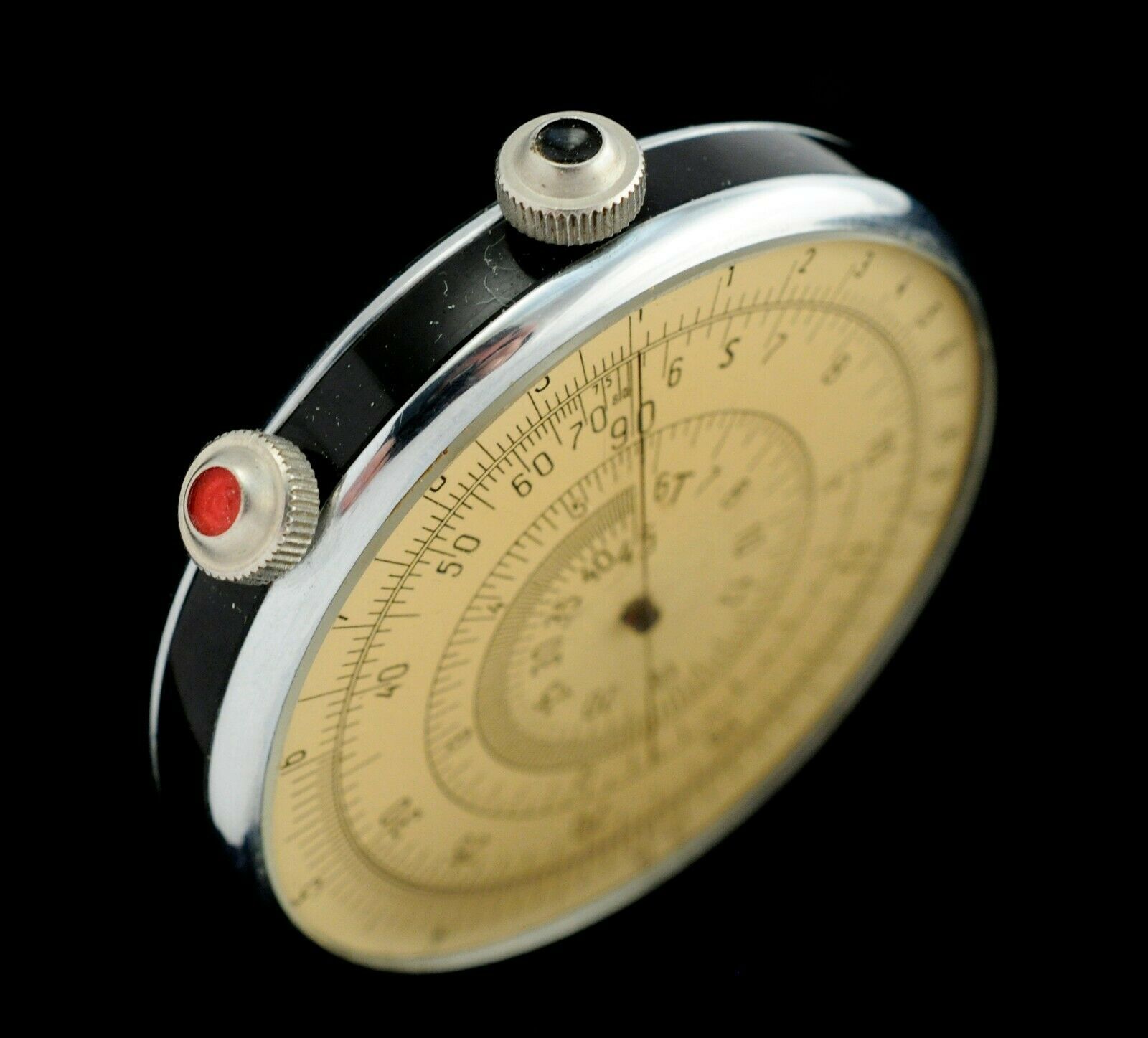
The logarithmic ruler consists of a body with two heads, two dials, one of which is rotated by means of a head with a black point and 2 arrows that rotate with a head with a red dot. Against the head with a black dot above the movable dial there is a fixed index.
On the moving dial there are 2 scales: internal - the main - counting and external - the scale of the squares of numbers.
On the fixed dial there are 3 scales: the outer scale is countable, analogous to the inner scale on the movable dial, the average scales of the "S" -values of angles for counting their sines and the inner scale of "T" -values of angles for counting their tangents.
Circular logarithmic ruler "KL-1"
1. The body.
2. The head with a black dot.
3. Head with a red dot.
4. The movable dial.
5. Fixed pointer.
6. The main scale (countable).
7. The scale of the squares of a number.
8. Arrow.
9. Fixed dial.
10. Counting scale.
Performing mathematical operations on the line "KL-1" is as follows:
I. Multiplication
Rotating the head with a black point, turn the movable dial to align the first factor on the counting scale with the pointer.
Rotate the head with a red dot to align the arrow with the mark "1".
Rotating the head with a black point, turn the mobile dial to align the second factor on the counting scale with the arrow.
Against the pointer over the counting scale, the desired value of the product is measured.
II. Division
Rotating the head with a black point, turn the mobile dial to align the divisible by the counting scale with the pointer.
Rotate the head with a red dot to align the arrow with the divider on the counting scale.
Rotating the head with a black point, turn the mobile dial to align the "1" mark with the arrow.
Against the pointer over the counting scale, count the sought value of the quotient.
III. Combined actions
Rotating the head with a black point, turn the movable dial to align the first factor on the counting scale with the pointer.
Rotate the head with a red dot to align the arrow with the divider on the counting scale.
Rotating the head with a black point, turn the mobile dial to align the second factor on the counting scale with the arrow.
Counter the pointer over the counting scale to calculate the final result.
Example: (2x12) / 6 = 4
IV. Square squaring
Rotating the head with a black point, turn the mobile dial to match the value of the number, erected in a square, along a counting scale with a pointer.
Against the same pointer on the scale of squares, read the desired value of the square of this number.
V. Extraction of the square root
Rotate the head with a black point to turn the mobile dial to match the value of the sub-root number on a scale of squares with a pointer.
Against the same pointer on the internal (countable) scale, read the desired value of the square root.
VI. Finding trigonometric functions of the angle
Rotating the head with a red dot align the arrow above the fixed dial with the value of the specified angle on the sine scale (scale "S") or on the scale of tangents (scale "T").
Against the same arrow on the same dial on the external (counting) scale read the corresponding value of the sine or tangent of this angle.
VII. Finding inverse trigonometric functions
Rotating the head with a red dot align the arrow above the stationary dial on the outer (counting) scale with the set value of the trigonometric function.
Against the same arrow on the scale of sines or tangents, read the value of the corresponding inverse trigonometric function.
VIII. Calculating the area of a circle
Rotate the head with a black point to turn the mobile dial to match the value of the diameter of the circle on the counting scale with a pointer.
Rotate the head with a red dot to align the arrow with the mark "C".
Rotating the head with a black point, turn the mobile dial to align the "1" mark with the arrow.
Against the pointer on the scale of squares, count the required value of the area of the circle.
We accept paypal.
I ship worldwide via Registered Airmail for
15$
. Usually delivery takes 12-18 days. Packaging is very safe.
Track Page Views With
Auctiva's FREE Counter